Tmp
Putting it all together -- Optimization and EPAnet
Prerequisites
- You should have completed the C++ programming primer preceeding this section.
- You have exposure to the EPAnet 2 software (graphical version is adequate).
- A basic understanding of Genetic Algorithms (Follow these links: [1],[2],[3] and spend some time if not.)
In this lesson, we push the abilities we have gained to the limit! We link two code libraries, namely, Evolving objects -- a versatile genetic algorithm code and EPAnet (toolkit) a pipe network calculation model by writing some relatively simple code and create a running program. The following section explains the problem we have selected to solve (please note that the problem itself is of secondary importance here, what we are trying to do is to hone the skills we have gained and build confidence to attack bigger coding projects).
Problem
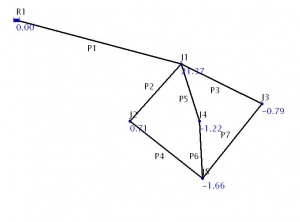
The figure on the left shows a water supply network with a reservoir, seven pipe segments conveying water and five junctions that have different demands. We want to compute the most economical pipe diameters for each segment while maintaining a minimum pressure head of 10 m at all junctions. You can open the File:Cbcpp pipe network1.inp in Epanet 2 software to view the network.
Our plan is to use a Genetic Algorithm to optimize the pipe diameters. For this we need to connect Epanet Software to a genetic algorithm code.
Plan
We will use the Epanet Toolkit, a programming interface designed to run Epanet 2.0 programmatically without the standard graphical interface. For the Genetic Algorithm part, we'll use Evolving objects a free and open source package for evolutionary computations.
Evolving objects can be downloaded from eodev] website. Epanet toolkit can be downloaded from [US-EPA]. However, for this exercise you may use the already downloaded versions of these tools. Download the file cbcpp_EO.zip into your computer and extract it to a new folder (say E:\GA\EO). This will create four subfolders,
code data eo-1.0 epanet_tools
We use code folder to keep all the code we write (not the code libraries we use!). It already have the files:
RealEA.cpp real_value.h
RealEA.cpp is a c++ program that can be used to access the EO Genetic algorithm functions. real_value.h has the cost function for the GA. We'll learn more about this later.
data folder where we shall keep all our data, has the water distribution network file.
eo-1.0 and epanet_tools have the evolving objects and epanet toolkit code libraries.
Solution
We shall attack our problem in a piecemeal fashion, in the steps given below:
- Get EO to solve a small GA problem.
- Replace the cost function with our own.
- Use epanet_toolkit to run Epanet on our water supply network and use the results to evaluate a cost function.
Usually this step-by-step approach is less error-prone than attempting the whole task once.
Running a GA
Create a new folder called projects under the same folder that has sub-folders of code, data, etc. This is where we shall keep the visual studio express edition related (platform specific) stuff. Open visual C++ and reate a new empty project EPGA in that folder. Add the following files in the code folder to the project.
RealEA.cpp real_value.h
When you try to compile the project, you will get the error message on the line:
#include <eo>
Indicating that the compiler can not include 'eo'. To remedy this, we should include the path to the include file eo ("..\..\eo-1.0.1\src"). This can be done by additing it to: Edit-><project>Properties->C/C++->General->Additional include directories.
At this stage RealEA.cpp should comile successfully, but would cause errors at linking stage. The error messages would look like
unresolved external symbol "public: virtual __thiscall eoFunctorStore::~eoFunctorStore(void)" (??1eoFunctorStore@@UAE@XZ) referenced in function "public: virtual void * __thiscall eoFunctorStore::`scalar deleting destructor'(unsigned int)" (??_GeoFunctorStore@@UAEPAXI@Z)
The reason for this is
- The compiler knows about eo library (by #include <eo>), but
- the real library objects of eo needed for linking are missing
To rectify this, we should let the linker access to the necessary libraries. Before doing this we have to make a detour. First save your project/solution and close it.
Building EO libraries
The eo code available for download does not have the libraries for windows built in, but they have the complete source and tools needed to build them. There is a visual C++ solution called eo.sln in the sub-folder win. Just build this solution (Project->Build solution). This will create the necessary libraries in the win.
One more point: It is beneficial to build the release version (not the debug version) of the libraries for performance reasons.
After this you will have the following libraries in the folder win\lib\release.
eo.lib eoes.lib eoga.lib eoutils.lib
Now open your project again. In add the above four files as dependancies for the linker. (Edit-><project>Properties->Linker->General->Additional Dependancies).
Then let the linker know where these are: (Edit-><project>Properties->Linker->General->Additional Library Directories). Add something like ..\..\eo-1.0.1\win\lib\release.
At this stage, you should be able to compile the project successfully. Debug->Start without Debugging should run the program, albeit with not-so-meaningful-at-the-moment results.
Enable debugging
If you try to debug your code at this stage, visual c++ 2005 will complain (as of 01:07, 9 April 2007 (JST)) that the binaries were not built with debug information. There is a separate article on how to enable debugging in visual studio 2005.
EO In-Action
Now is a good time to have an idea about how our GA code works. Don't worry if you can not understand everything -- what is important is to have a general idea of how things work!
The actual code-in-action is very short, indeed. I have changed the comments a little bit.
/* Many instructions to this program can be given on the command line.
The following code understands what you have specified as command line arguments.
*/
eoParser parser(argc, argv); // for user-parameter reading
eoState state; // keeps all things allocated
typedef eoReal<eoMinimizingFitness> EOT;
// The evaluation fn - encapsulated into an eval counter for output
eoEvalFuncPtr<EOT, double, const std::vector<double>&>
mainEval( real_value );
eoEvalFuncCounter<EOT> eval(mainEval);
// the genotype - through a genotype initializer
eoRealInitBounded<EOT>& init = make_genotype(parser, state, EOT());
// Build the variation operator (any seq/prop construct)
eoGenOp<EOT>& op = make_op(parser, state, init);
// initialize the population - and evaluate
// yes, this is representation indepedent once you have an eoInit
eoPop<EOT>& pop = make_pop(parser, state, init);
// stopping criteria
eoContinue<EOT> & term = make_continue(parser, state, eval);
// output
eoCheckPoint<EOT> & checkpoint = make_checkpoint(parser, state, eval, term);
// algorithm (need the operator!)
eoAlgo<EOT>& ea = make_algo_scalar(parser, state, eval, checkpoint, op);
make_help(parser); //print help, if something is missing or user gives /h
// evaluate intial population AFTER help and status in case it takes time
apply<EOT>(eval, pop);
// print it out
cout << "Initial Population\n";
pop.sortedPrintOn(cout);
cout << endl;
run_ea(ea, pop); // run the ea
cout << "Final Population\n";
pop.sortedPrintOn(cout);
cout << endl;
You can get away without understanding a single line of code above!! The only critical part is the following function, specified in the header file real_value.h. In order to adopt these versatile algorithms to solve a problem of our choosing, only changing this header file is adequate.
Fitness function
double real_value(const std::vector<double>& _ind)
{
double sum = 0;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < _ind.size(); i++)
sum += _ind[i] * _ind[i];
return sqrt(sum);
}
The eo library expects this function to be present and uses to evaluate the individuals in the population for fitness.
What happens here?
- Our genotype vector has (say) n number of items. The fitness function simply squares each of these and add them up and returns the square root. No rocket science here! Just, the rule here is larger the individuals -- better the fitness!!
- The GA code does the rest,
Try running the algorithm. It will go on decreasing the cost function and exit at 100th generation. The default is 100 generations, in a moment, we'll get into the details on how to change the default behavior.
Providing arguments
Once you run the above code once successfully, check the folder that consists the executable file (project\EPGA\Debug folder). There should be a file EPGA.exe.status EO library creates this file, when you run the program. It lists all the changes you can make at the runtime to the GA. (Meaning, you don't have to recompile the program -- just indicate the parameters.) There are two ways of specifying parameters -- first is to list them in the command line. For example try the following in the dos prompt.
EPGA.exe --help
It will just print a long help message. Then try
EPGA.exe --maxGen=1000
It will run a GA like before, but will stop only after 1000 generations.
EPGA.exe --maxGen=0 --steadyGen=20
will run the GA until 20 generations without any improvement.
So, you get the idea.
Now try this. First copy the file EPGA.exe.status to args.txt and edit the latter with notepad.
> copy EPGA.exe.status args.txt
> notepad args.txt
Notice that this file has all the arguments that can be given at the command line. # in a line means the rest that follows is a comment. Note that almost all the argments are commented. Now make sure only the following items are uncommented.
--vecSize=3
--maxGen=0
--steadyGen=20
Now, run the program with the following command.
EPGA.exe @args.txt
Notice that this is equivalent to running
EPGA.exe --vecSize=3 --maxGen=0 --steadyGen=20
Within Visual Studio
To make things a bit easier for us, lets do the following. Move the file args.txt to the data folder.
> move args.txt ..\..\data\.
Then in your project in visual C++, add the file data.txt to resource files tab, in solutions explorer. (This step is optional)
Finally, add the following
@..\..\data\args.txt
to the Command argments Configuration properties->Debugging.
Now within visual C++ itself, you can just modify the file args.txt to suit your needs, save it and re-run our program.
Writing our own cost function
Now let's turn into our original problem. We need to minimize the diameter of seven pipes while maintaining reasonable (>10m) pressure at all supply nodes. Lets forget the pressure part for a moment and concentrate on minimizing the diameter. (The answer here is obvious, if pressure is no concern, then the 'best' diameter is zero!! -- but let's live with this silly notion for the moment.)
Do the following changes:
- First we change the args.txt file to have
--vecSize=7 # we have seven pipes, each diameter can be represented by a single real value.
--initBounds=7[0,500] # -B : Bounds for variables -- pipe diameter within 0-500mm
--objectBounds=7[0,500] # -B : Bounds for variables -- pipe diameter within 0-500mm
- Change the cost function real_value.h to the following:
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
double real_value(const std::vector<double>& _ind)
{
//GA returns diameter as ind_
double length=1000;
double factor=1.; //some factor so that cost=length=diameter*factor (lets keep things simple!)
double dia,cost = 0;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < _ind.size(); i++){
cost+=_ind[i]*length*factor;
}
return cost/10000;
}
If everything is all right, you will have some large initial cost, and a very small final cost.
Now that we have customized the GA to represent our silly optimization problem, it is but a small step to do the real job!
In comes EPANet 2
With the provided EPANET toolkit (in epanet_tools folder) there is a help file: TOOLKIT.HLP. This is going to be our standard reference to various calls to epanet program via toolkit.
Let's do most of the changes in the real_value.h file and try to keep changes in RealEA.cpp to a minimum.
We will focus on several toolkit functions:
ENOpen and ENClose
- Declaration
int Nopen( char* f1, char* f2, char* f3)
- Description
- Opens the Toolkit to analyze a particular distribution system.
- Declaration
;Description:Closes down the Toolkit system (including all files being processed). ===ENSolveH=== ;Declaration: int ENsolveH( void ) ;Description: Runs a complete hydraulic simulation with results for all time periods written to the binary Hydraulics file. ===ENGetNodeValue=== ;Declaration:int ENgetnodevalue( int index, int paramcode, float* value ) ;Description:Retrieves the value of a specific link parameter. ===ENSetLinkValue=== ;Declaration:int ENsetlinkvalue( int index, int paramcode, float value ) ;Description:Sets the value of a parameter for a specific link. ==Call EPANet 2== Do the following changes in RealEA.cpp. <source lang=cpp> try { // first initialize the Epanet epanet_init(); // <-- new addition eoParser parser(argc, argv); // for user-parameter reading ... // close Epanet epanet_close(); // <-- new addition } catch(exception& e)
Now let's do the major modifications in real_value.h
As the first stage:
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include "epanet2.h"
double dia_cost_factor=1.; //some factor so that cost=length=diameter*factor (lets keep things simple!)
using namespace std;
double real_value(const std::vector<double>& _ind)
{
//GA returns diameter as ind_
double length=1000;
double dia,cost = 0;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < _ind.size(); i++){
cost+=_ind[i]*length*dia_cost_factor;
}
return cost/10000;
}
void epanet_init(){
int ret;
char file[500]="../../data/network.inp";
char rept[500]="../../data/network.rep";
ret=ENopen(file,rept,"");
cout << "At opening Epanet retured : "<<ret<<'\n';
}
void epanet_close(){
int ret;
ret=ENclose();
cout << "At closing Epanet retured : "<<ret<<'\n';
}
To run the above you will have to
- Add ..\..\epanet_tools to additional include directories.
- Add epanet2vc.lib to additional dependencies.
- Add ..\..\epanet_tools to additional library directories (At this stage the application should compile, but will give a runtime error.)
- Add PATH=%PATH%;..\..\epanet_tools to debugging environment. (Project properties->Debugging->Environment)
Run the application at this stage to make sure that the two epanet calls return zero (error free call signal).
Then add a function pressure_cost to real_value.h to compute the 'cost' of pressure deficiency. (Something like the one below)
double pressure_cost(vector<double> _ind){
int ret;
double cost;
for(unsigned int i=0;i<npipes;i++){
int index=-1;
ret=ENgetlinkindex(pipes[i],&index);
//cout << "At opening Epanet retured : "<<ret<<'\n';
ret=ENsetlinkvalue(index,EN_DIAMETER,_ind[i]);
//cout << "At opening Epanet retured : "<<ret<<'\n';
}
//now run the simulation
ret=ENsolveH();
//cout << "At solve Epanet retured : "<<ret<<'\n';
cost=0;
//read the pressure values
for(unsigned int i=0;i<nnodes;i++){
int index=-1;
ret=ENgetnodeindex(nodes[i],&index);
float value;
//cout << "At ENgetnodeindex Epanet retured : "<<ret<<'\n';
ret=ENgetnodevalue(index,EN_PRESSURE,&value);
//cout << "At ENgetnodevalue Epanet retured : "<<ret<<'\n';
if(value<10){
cost+=pressue_cost_factor*(10-value);
}
}
//cout << "At ENcloseH Epanet retured : "<<ret<<'\n';
return cost;
}
The value of variable pressure_cost_factor should be carefully considered (against that of dia_cost_factor).
At this stage you have a complete living-breathing program that join the power to evolving objects with Epanet.